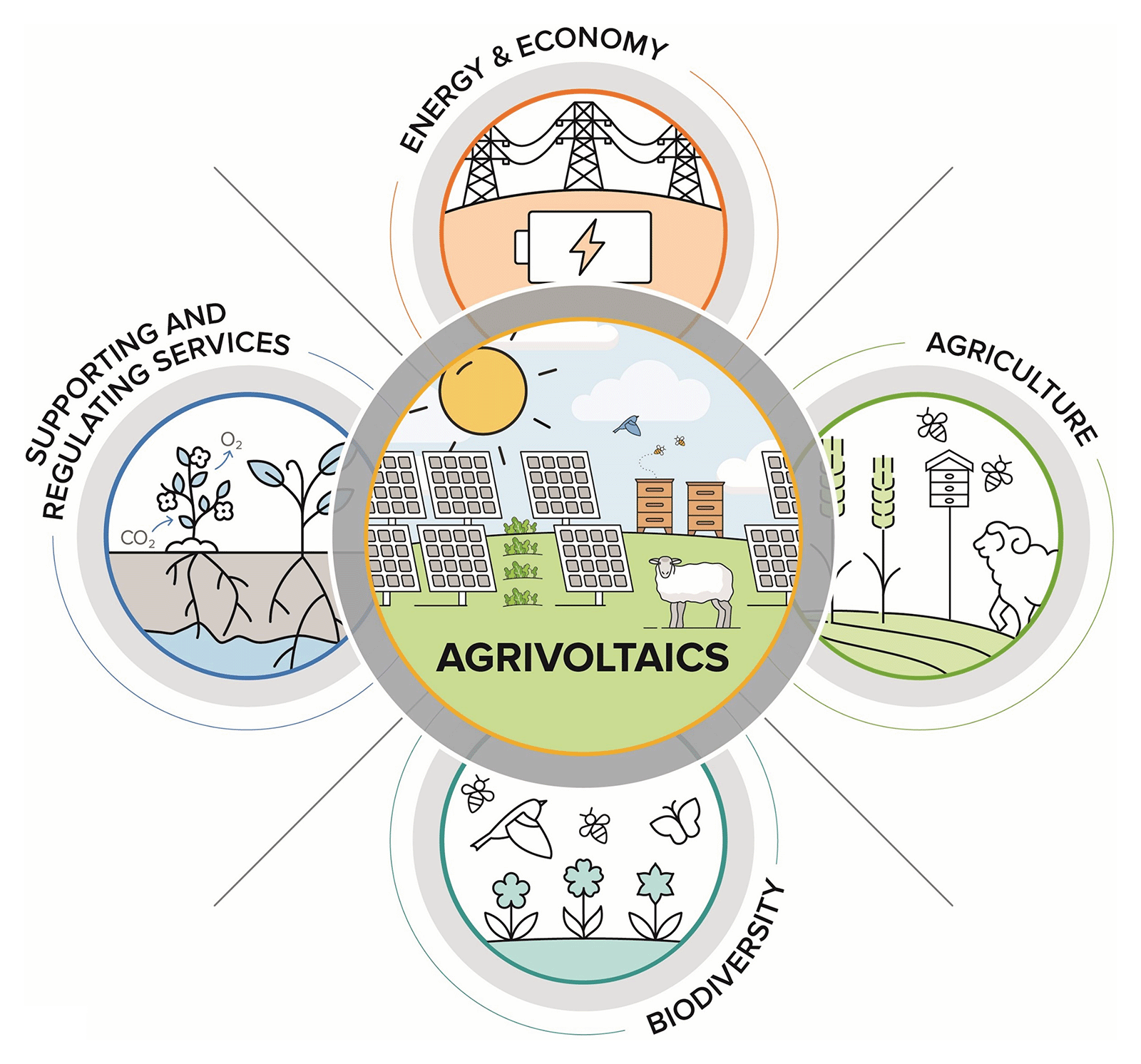
The Science
A group of researchers set out to synthesize what is currently known about the ecosystem services of agrivoltaic (AV) systems. AV systems bring agriculture and vegetation management together with ground-mounted solar development to improve a solar site’s land use efficiency. The researchers looked at three kinds of AV systems: solar facilities combined with either crops, livestock grazing, or habitat restoration. The different combinations on a solar site can increase the ecosystem services output. Ecosystem services are generally described as goods and services humans receive from the environment, including energy and food production, biodiversity conservation, and supporting and regulating services (such as runoff control and carbon sequestration). Researchers set out to clarify what specific opportunities exist for these systems to achieve energy, ecosystem, and sustainability goals.
The Impact
AV systems are a promising approach to optimize land use productivity. They can maximize the ecosystem service outputs of solar energy production. They can also help reduce the negative interactions between climate change and agriculture (for example, by retaining more water and providing shading for plants in areas where temperature is increasing and rainfall is decreasing). Although AV systems align with several international sustainable development goals, this article found several challenges and information gaps that need to be addressed to maximize ecosystem services. Understanding these gaps is important for all stakeholders to be able to implement AV systems at industry scale. To get to this point, stakeholder partnerships will be crucial to integrating solar and agriculture components into project designs early on. In addition, these partnerships may be useful in providing recommendations to policymakers on the creation of incentives for AV systems.
Summary
Ground-mounted solar energy facilities require large amounts of land. Therefore, the sustainability of these developments may depend on formulating dual land use strategies that maximize the outputs of solar energy production and other land uses. One such strategy – often termed agrivoltaics (agriculture + ground-mounted solar) – has emerged as a promising dual use strategy that co-locates solar energy production with agricultural and vegetation management practices to increase the ecosystem service output of solar sites.
But what are agrivoltaic (AV) systems in practice and what are the more specific opportunities for these systems to achieve energy, ecosystem, and sustainability goals? A September 2022 article published in the journal Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems synthesized the broad applications of AV systems, including the following:
- Solar-cropping systems: The co-location of solar facilities and crop production whereby crops are grown under or between the solar infrastructure (for example, rows of photovoltaic panels).
- Solar-animal systems: The co-location of solar facilities and animal husbandry and livestock grazing.
- Solar-habitat systems: the co-location of solar facilities and habitat restoration through re-establishing deep-rooted flowering plant species under and around the solar infrastructure.