Scientific Achievement
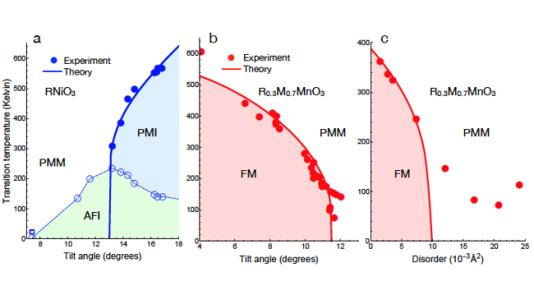
We have produced a phenomenological but quantitative model to explain the atomic size-dependence of metal-insulator transitions in transition metal oxides.
Significance and Impact
The Mott transition temperature in transition metal oxides is strongly dependent on cation atomic size. Our theory explains this by long-range coupling of local lattice distortions via elastic degrees of freedom. Our simple parameterized classical model may be a way to understand and tune long-range correlations.
Research Details
- We produced a free energy functional by parameterizing the local many-body potential energy surface, and coupling these local degrees of freedom through explicit long-range elastic couplings of the local modes, elastic distortions, and rotations.
- The statistical physics model was solved in a self-consistent-field approximation, allowing for a determination of the transition temperature as a function of both average atomic size, and disorder.
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology. The nation’s first national laboratory, Argonne conducts leading-edge basic and applied scientific research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne researchers work closely with researchers from hundreds of companies, universities, and federal, state and municipal agencies to help them solve their specific problems, advance America’s scientific leadership and prepare the nation for a better future. With employees from more than 60 nations, Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science.
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit https://energy.gov/science.