Express Licensing
- Thermal Multi-layer Coating Analysis (IN-05-125), (IN-14-032)
The Invention
Pulsed thermal imaging is widely used for nondestructive evaluation of advanced materials and components. Thermal imaging methods to analyze single-layer materials are well developed. However, a general method for analyzing multi-layer materials and coatings/films has not been developed due to the complexity of material systems and lack of an analytical solution. This technology provides a general method, test system including a filter, and numerical algorithm for automated analysis of thermal imaging data for multi-layer coating materials.
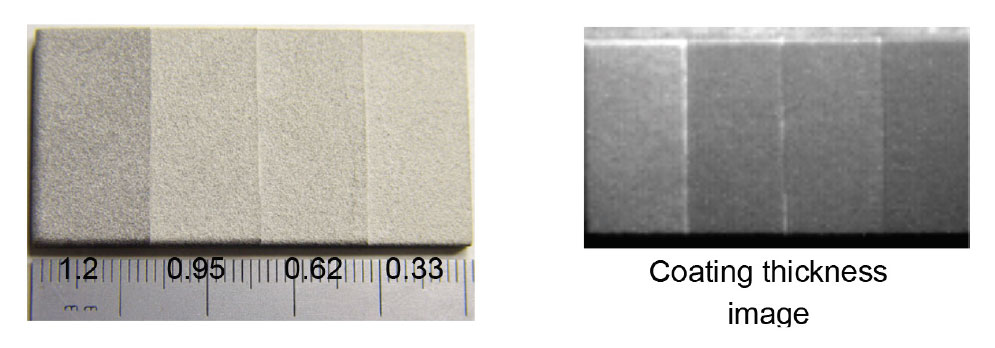
Argonne’s pulsed thermal imaging-multilayer analysis method can accurately measure coating thermal conductivity and heat capacity (and/or thickness) distributions over an entire component’s surface. The method analyzes a temporal series of measured thermal imaging data to determine the properties for all coating layers based on a multilayer model. Argonne’s invention is currently the only method that can analyze coatings of more than one layer, is fully automated to produce 2D layer property images, and has validated high accuracy.
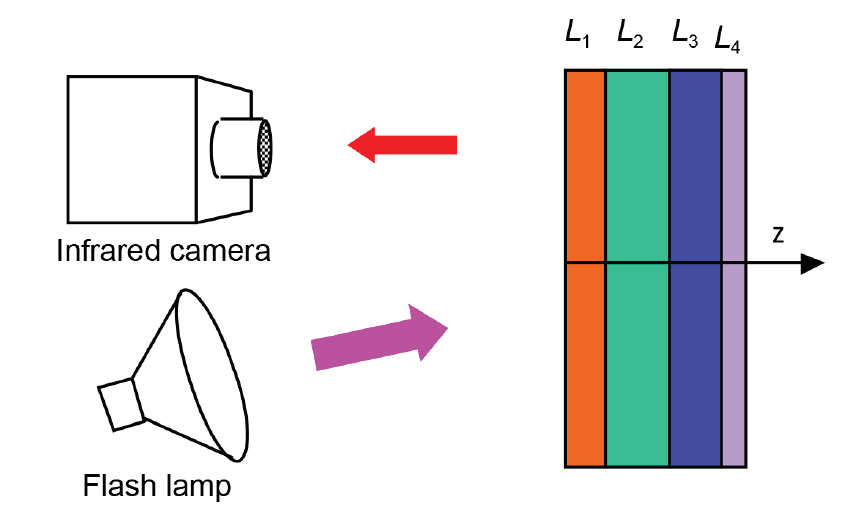
Argonne’s approach includes an infrared filter for flash lamps to eliminate the flash’s infrared radiation, ensuring accurate detection of surface temperature during pulsed thermal imaging tests.
Key to Argonne’s thermal multi-layer analysis method is the numerical algorithm used for automated analysis of thermal imaging data for multi-layer materials, implemented in dedicated, Argonne-created software that allows for complete data-processing automation without the need of user intervention.
Benefits
- Allows fast 2D imaging of multi-layer material properties of an object from one surface
- All-in-one solution that includes method, optical filter, and analytical software for thermal multi-layer material analysis
- Imaging is nondestructive and fast
- Eliminates infrared radiation to assure data accuracy
- Automated analysis of imaging data
Applications and Industries
- Multi-layer coating materials development
- Manufacturing quality control
- Coating degradation monitoring
- Medical applications
Developmental Stage
Proof of Concept: the technology has been tested and proven to work for coated engine parts.
Argonne Inventions
- IN-05-125, Optical Filter for Flash Lamps in Pulsed Thermal Imaging View the patent.
- IN-14-032, Method and Apparatus for Material Thermal Property Measurement by Flash Thermal Imaging View the patent.
- IN-06-017, Method for Thermal Tomography of Thermal Effusivity from Pulsed Thermal Imaging View the patent