In a study published in Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, researchers report that loss mechanisms in grain boundaries of the photovoltaic material CdTe can be reduced by use of select dopants.
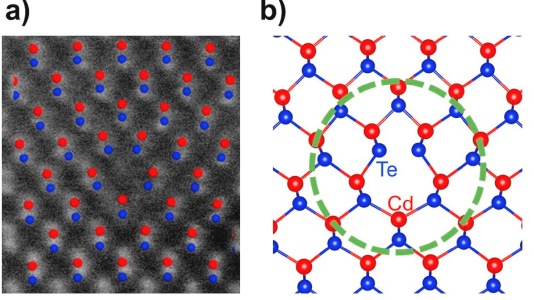
(a) Scanning tunneling electron microscopy image with structural model and (b) structural model with dislocation core region (grain boundary regions) circled (Cd = red circles, Te = blue circles).
Scientific Achievement
Systematic computational modeling showed that loss mechanisms of charge trapping and recombination within the grain boundaries of polycrystalline CdTe can be reduced by incorporation of specific atomic dopants. The greatest performance improvement (reduced charge recombination) was achieved with co-doping, specifically substituting Te with Se and Cd with Cu or Al.
Significance and Impact
The findings could help improve photovoltaic devices based on polycrystalline CdTe, the second most-widely deployed photovoltaic material due to its relatively high efficiency and low manufacturing cost./p>
Research Details
- Computations were performed in Carbon, a high-performance computing cluster at the CNM.
- Corresponding Author: Maria Chan, CNM staff scientist
- Sponsor: US DOE SunShot program
Work was performed in part at CNM.