Nuclear fusion has long promised to provide a safe and clean source of virtually limitless energy. Developing efficient devices that fulfill that potential, sustainably, demands a scientific and engineering effort that is a major area of plasma physics research today.
A tokamak is an experimental machine designed to harness the energy of fusion using a powerful magnetic field to confine plasma in the shape of a torus (a doughnut-like shape). Achieving a stable plasma equilibrium requires precise control of the magnetic field lines that wind around the torus in a helical shape.
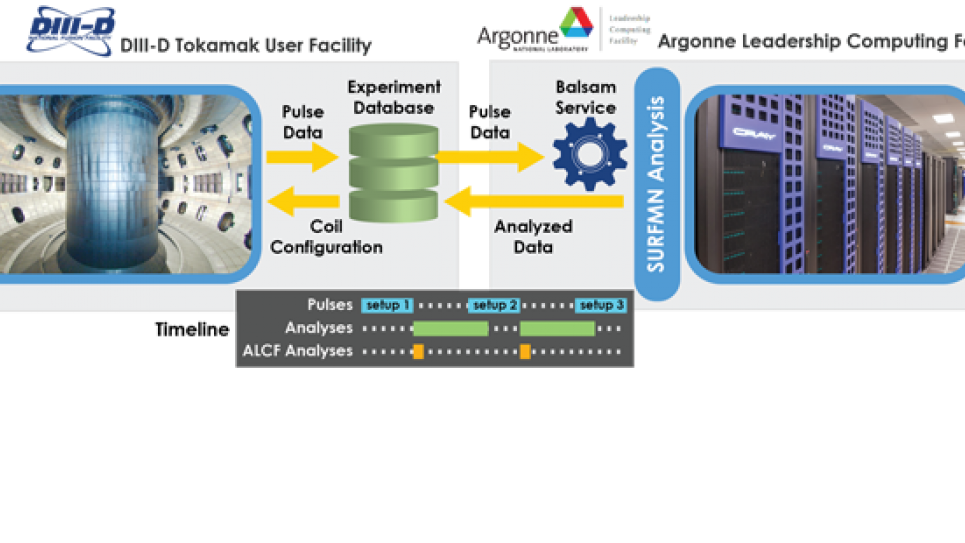
Argonne researchers led a successful integration effort with the DIII-D National Fusion Facility, a DOE Office of Science User Facility in San Diego.
To study magnetic confinement in fusion energy, DIII-D scientists conduct fast-paced plasma physics experiments that involve creating six-second pulses of confined plasma every 15 to 20 minutes. Planning for each new pulse is informed by data analysis of the previous pulse.
To help the DIII-D team obtain these results on a between-pulse timescale, the Argonne team automated and shifted the analysis step to computing systems at the Argonne Leadership Computing Facility. The effort computed the analysis of every single pulse and returned the results to the research team in a fraction of the time required by the computing resources locally available at DIII-D.
Learn more about Argonne’s work with DIII-D.